


Next: Plot Functionality
Up: Plots
Previous: Plots
Contents
Subsections
To draw a 3D plot of three different columns,
- Select the column to be plotted on the X-axis in ``X:
'' labeled combobox.
- Select the column to be plotted on the Y-axis in ``Y:
'' labeled combobox.
- Select the column to be plotted on the Z-axis in ``Z:
'' labeled combobox.
- Click on ``3D Scatter Plot'' icon
 of the toolbar.
of the toolbar.
You can see the 3D scatter plot. If required, user can apply log and
reversed axis functionality as described in ``Plot
Functionalities -> Log'' & ``Plot
Functionalities -> Reverse''.
Figure 1:
3D Scatter Plot
|
|
Overlay:
This part is described in ``Overlay''
section under ``Plot Functionalities'''
``Common to All Plots''.
To draw the histogram of one column against another,
- Select the column on X-axis.
- Select the column on Z-axis.
- Click on ``3D Histogram'' icon
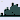 of the toolbar.
of the toolbar.
A sample histogram is shown in Figure 2.
If required, user can apply log and reversed axis functionality as
described in ``Plot Functionalities -> Log''
& ``Plot Functionalities -> Reverse''.
Overlay:
This part is described in ``Overlay''
section under ``Plot Functionalities'''
``Common to All Plots''.
Surface can be made using an equation or by loading a file which has
regular grid data. If the surface is being made from a data file,
then user can choose between Bi-Linear and Bi-Cubic Spline interpolation.
To draw the surface using an equation
- Click on the ``Surface Plot'' icon
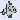 of the toolbar.
of the toolbar.
- Click the Equation icon
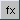 in the toolbar
of the Surface Plot Dialog. This launches an equation maker dialog.
in the toolbar
of the Surface Plot Dialog. This launches an equation maker dialog.
- Enter the equation in the equation maker dialog. We use $a and $b
as variables. Eg: sin($a)*sin($b)
- Then enter the ranges for a, b & c. The range for ''c'' is indicative.
The actual range may differ. User has to play around with the Y range
a little bit using the PlotProperties dialog (launched by clicking
 on the toolbar of Surface Plot
dialog) after the surface is drawn
on the toolbar of Surface Plot
dialog) after the surface is drawn
While variables a,b make the XZ plane, c defines the height of surface
at an (a,b) on the Y-Axis
- Click Plot button to draw the surface.
Shown below is the Equation maker dialog
To draw a surface plot using a data file,
- load the data file. The file should have atleast three columns (say
a, b, c) in row-by-row format as shown below
a1, b1, c11
a1, b2, c12
a1, b3, c13
...
a2, b1, c21
a2, b2, c22
a2, b3, c23
...
- click on the ``Surface Plot'' icon
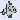 of the toolbar.
of the toolbar.
- In the surface plot, the base plane is XZ plane and height axis is
the Y-Axis. (For convenience the combo (drop down) boxes are ordered
X, Z, Y).
Select the columns in X and Z axis comboboxes. (In the example given
in point#1 (a,b,c) map to (x, z, y))
- Then selectc the Y-Axis combo box.
- To determine the Y value for a particular (X,Z) we interpolate the
Y values of near by (X,Z) points from the data file. User can choose
betweenm BiLinear or BiCubic Spline interpolation from the Interpolation
combo box.
- Clicking ``Plot'' button draws
the surface plot.
- You can use the MeshLine multiplier combo boxes to change the number
of mesh lines to be drawn. Value can vary from 0.1 to 1 insteps of
0.1
- You can use the Smoothness combo boxes to smoothen the surface. Value
can vary from 1 to 2 in steps of 0.1. Higher the value the surface
is more smooth and the time taken to render the surface is more.
A sample surface plot is shown in Figure 4.
Setting ``Smoothness'' changes
the number of block counts on X axis, while ``Mesh
Line multiplier'' represents number of blocks on
Y axis. The smoothness or mesh line multiplier values can be set in
the range between 0-2.
Enter line of sight in Plot:
You can set the line of sight of all the three axis by clicking of
``Enter Line of Sight'' sub menu
of ``View'' menu. Clicking on this
sub menu prompts up a dialog which shows three angles Theta, Phi and
Psi. Theta, Phi and Psi are angles from the line of sight to the X,
Y and Z axis respectively. Changing their values and clicking on ``Apply''
applies changes to the cubic grid of plot.
The Enter Line of Sight dialog is shown below in figure 5
given above.
Figure 5:
Enter Line of Sight
|
|



Next: Plot Functionality
Up: Plots
Previous: Plots
Contents